Researchers now estimate how a lot “white gold” could also be present in southern Arkansas’s huge lithium reserves: as much as 19 million tons, or sufficient to fulfill the projected 2030 world demand 9 instances over.
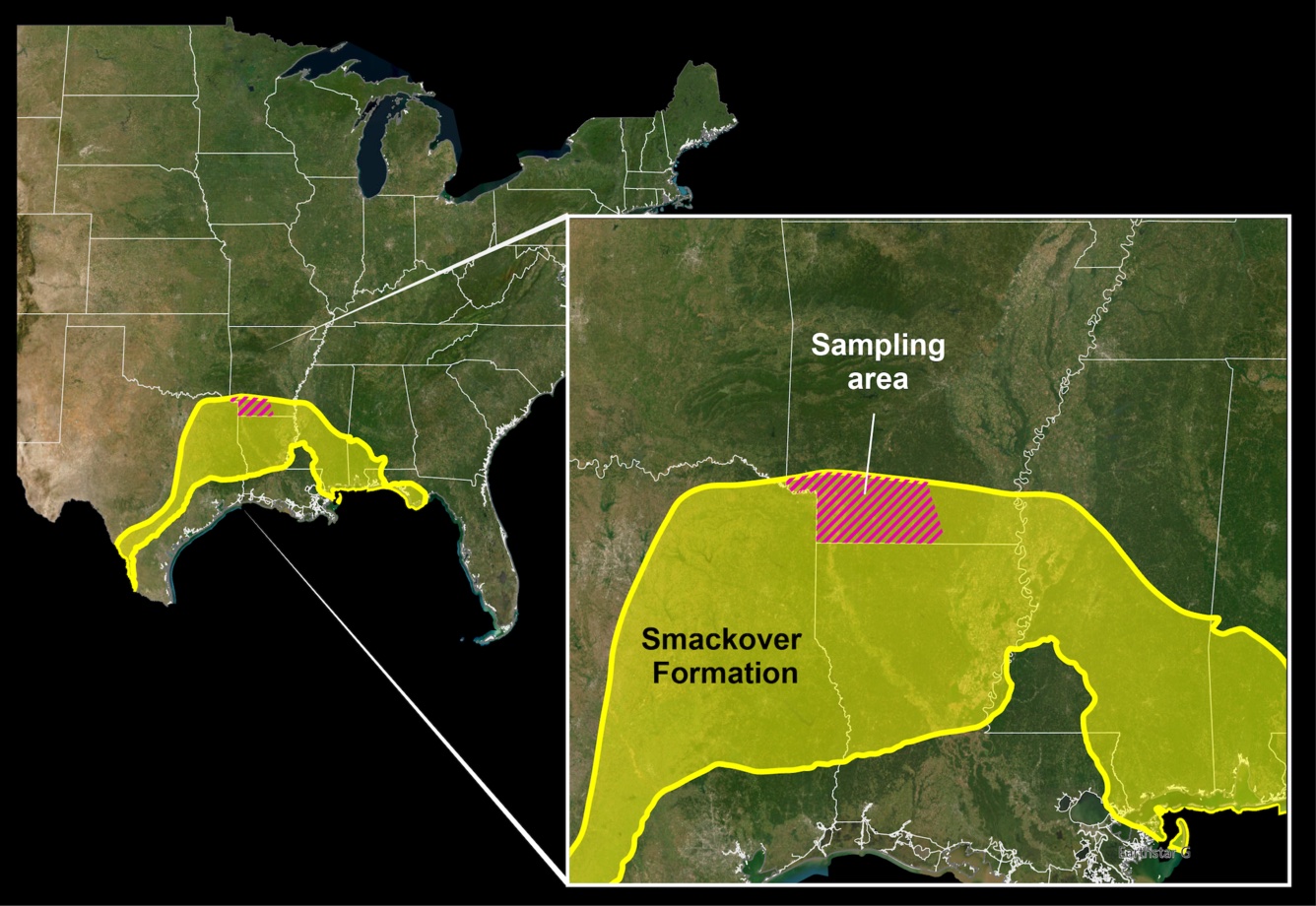
United States Geological Survey (USGS) researchers used water testing and machine studying to get an estimate of what is likely to be present in an underground brine within the Smackover Formation in southern Arkansas, a relic of an historical sea that’s now an enormous limestone formation that stretches from Texas, Louisiana, Arkansas, Alabama, Mississippi, and into Florida. The researchers introduced that it may include anyplace from 5 million to 19 million tons of lithium.
“If commercially recoverable, the quantity of lithium current would meet projected 2030 world demand for lithium in automotive batteries 9 instances over,” the researchers mentioned in a information launch.
Revealed within the journal Science Advances, the examine cites that the lithium present in southern Arkansas may make as much as 36% to 136% of the present US lithium reserve estimate – after all, that’s a sweeping quantity, however we get the gist. Loads of lithium, however the issue is the best way to get it out.
Lithium extraction – a nascent business within the US – often entails open-pit drilling and creating big evaporation swimming pools, all which might take months and years and depart destruction of their wake. Final yr, ExxonMobil acquired the rights to 120,000 gross acres of the Smackover formation in southern Arkansas and have been utilizing oil and fuel drilling strategies to entry the saltwater brine about 10,000 toes underground.
To extract the lithium, the corporate makes use of direct lithium extraction (DLE) know-how, during which brine is pumped to the floor, then lithium and different minerals are extracted earlier than sending the water again underground. It’s touted as extra environmentally pleasant, however local weather activists say the know-how is largely untested and query the hazard of utilizing it at scale and the way it may have an effect on the water provide. Exxon has mentioned that it goals to enter manufacturing in 2027, in keeping with a report within the New York Instances, and “to be churning out sufficient lithium by 2030 to provide greater than 1,000,000 electrical automobiles per yr.”
In fact, there are different hurdles. In line with the Arkansas Instances, 5 companies in complete have been trying to begin extracting lithium in southern Arkansas, and are at present locked in a dispute with landowners over how a lot to pay for mineral rights. The businesses – Albemarle Company, ExxonMobil, Normal Lithium, Lanxess, and Tetra Applied sciences Inc. – filed a joint software in late July to set a royalty charge of 1.82%, which landowners say would enable the businesses to illegally bypass the state’s rulemaking course of.
To get to their estimates, researchers took samples from Arkansas and analyzed them on the USGS Brine Analysis Instrumentation and Experimental lab in Reston, Virginia, after which in contrast them with information from historic samples throughout the USGS Produced Waters Database of water from hydrocarbon manufacturing. Utilizing machine studying, researchers mixed lithium concentrations in brines with geological information to create maps that predict complete lithium concentrations throughout the area, even in areas missing lithium samples.
“Our analysis was in a position to estimate complete lithium current within the southwestern portion of the Smackover in Arkansas for the primary time,” mentioned Katherine Knierim, a hydrologist and the examine’s principal researcher. Whereas noting that the estimates are “an in-place evaluation,” she provides that they “estimate there may be sufficient dissolved lithium current in that area to interchange US imports of lithium and extra.”
Picture: Courtesy of the US Geological Survey
Learn extra: A California lake has sufficient lithium to energy 375 million EVs
FTC: We use revenue incomes auto affiliate hyperlinks. Extra.



